Overview
Stud welding is a complete one-step fastening system, using fasteners called weld studs. Weld studs come in a variety of designs, threaded, unthreaded, tapped, etc., sizes and shapes for a wide range of applications.
Examples of Weld Studs:
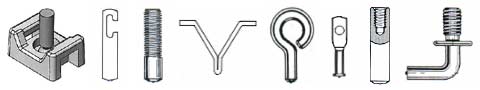
A weld stud can be end-joined to a metal work piece instantaneously for a high quality, high strength permanent bond.
The base metal and the welded fastener do not need to be the same material. For example these combinations can be welded together - brass to copper, brass to steel, copper to steel and similar combinations.
Stud welding is less expensive than other fastening methods and can used in locations which do not allow the use of other fasteners. Weld studs can be installed by one man, working on one side of the work piece, in less than a second.
There are many reasons why the stud welding process is superior over other fastening systems.
Industries using Stud Welding
Weld Studs fasteners are used in a wide variety of industries:
Aerospace
Appliances
Automotive
Construction
Electronics
Forging Process
Insulation Installation
Light and Heavy Duty Equipment
Offshore
Petrochemical
Shipbuilding
Signs and Decorative Trim
Toys
Transportation
Utilities Metalworking
Stud Welding Equipment
The equipment required for stud welding is composed of the following:
A direct current Power Supply
A Controller
A Weld Gun
Cables to tie the system components and base metal together
In most systems, the power supply and controller are combined as one component called the "Welder".
Two Methods for Stud Welding
Two stud welding methods are available - Arc Stud Welding and Capacitor Discharge (CD) Stud Welding. The method used depends on the type of stud fastener needed based on the application and the base metal the fastener well be welded to.
Arc Stud Welding Process
Arc Stud Welding is generally used to weld large diameter fasteners to rougher and thicker base metals.
Arc Studs may be almost any shape and there are literally hundreds, however, they must have one end of the fastener designed for Arc welding equipment.
Mild steel, stainless steel and aluminum are applicable materials for Arc welding.
1.
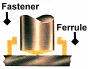
A fastener and ceramic ferrule are firmly placed against the work surface under spring tension.
2.

Upon triggering, the weld gun automatically lifts the fastener from the base metal and initiates a controlled electric arc which melts the end of the fastener and a portion of the base metal.
3.

A ceramic arc shield concentrates the heat and retains the molten material in the weld area for maximum weld strength and reliability.
4.

At the precise moment the fastener and the parent metal become molten, the fastener is automatically plunged into the work surface. The metal solidifies and a high quality fusion weld is completed.
How a Weld Stud Fastener is Installed
1. Load

The fastener is manually or automatically inserted into the stud welder chuck.
2. Position

The fastener is positioned into firm contact with the work surface.
3. Fire

The welding gun is activated and the fastener is welded in a fraction of a second. The fastener weld develops full strength instantly.